What is Absolute Advantage? Examples and Theory
The concept of absolute advantage has been used throughout history to justify the privileges of certain countries or businesses. For example, during the Industrial Revolution, England was said to have an advantage over other countries because of its abundant natural resources. Today, absolute cost advantage is still used to explain why some countries or businesses are successful while others are not.
The law of absolute advantage is applicable in business and the economy of nations. You have an absolute advantage whenever you have something that makes you more productive that others don’t have.
What is absolute advantage?
Absolute advantage theory of international trade
The absolute advantage theory is an economic theory that states that there is a country or business that has an unfair advantage over other businesses or countries. This advantage is due to the fact that the company or country has a capability or tool that other businesses or countries don’t have. The theory of absolute advantage explains why some countries are able to create more wealth than others; or why certain businesses are successful.
Adam Smith’s theory of absolute advantage
The theory of absolute advantage was founded by Adam Smith in 1776 when he published the book “The Wealth of Nations“. Adam Smith brought up the concept of absolute advantage to counter mercantilism.
Smith’s theory of absolute advantage states that all nations would gain simultaneously if they practiced free trade and specialized in accordance with their absolute advantage.
Adam Smith argued that it was not possible for all nations to be wealthy at the same time by following mercantilism (which encourages exports but discourages imports by using instruments such as tariffs and imperialism).
Adam Smith’s absolute advantage theory is based on the idea of productivity of labor when comparing two nations. The problem with this concept is that the possible gains of trade between two countries are not mutually beneficial. The country with absolute cost advantage gains, with little or no gains for the other.
Disadvantages of absolute cost advantage theory
- There are no mutual benefits: the country with the absolute advantage has more potential gains from trade.
- The absolute advantage principle creates an imbalance in the market; with most of the market share being captured by the country with the advantage.
- Countries with an absolute cost advantage can take advantage of other countries because they have more resources than those other countries.
Assumptions of absolute cost advantage theory
- The absolute advantage theory assumes that free trade always exists between countries without taking note of policies such as trade protectionism.
- It assumes the country with the most resources can always produce the most goods at the lowest cost. That is, the country or industry with the absolute advantage can produce goods and services more cheaply than other countries or industries.
- The country or industry with the absolute cost advantage can export its goods and services to other countries or industries more easily than other countries.
- It assumes that there is a fixed amount of resources available to each country.
- That each entity has the same level of knowledge and skill about how to use its fixed resources. That is, there is an unlimited ability to produce goods and services.
- Another assumption of the theory is that the costs of production for each entity are equal.
- There is no technological progress or transfer of technology between countries; this means that a country with an absolute cost advantage in technology would continue to do so without other countries catching up; or that other countries and industries are unable to copy the product, technology, or process used by the country or industry.
- Countries are independent and free to trade goods and services without restrictions.
- Output per unit of input is maximized.
- There are no transaction costs associated with producing goods.
These are a few assumptions that underpin absolute advantage theory. An entity in this theory can be a business, a country, or an individual. While this theory may thoughtful, it is not always true and accurate because some of these assumptions are false in practice.
Problems and criticism
- The theory is not applicable to multilateral trading between countries. It assumes international trade must occur between two countries alone.
- Free trade does not always occur in international trade because most countries would prefer to export and reduce their imports. To reduce imports, the government often adds tariffs to imported products in order to discourage imports.
Factors that determine absolute cost advantage
There are factors that determine the advantage that one country has over another. These include:
- Resources: the country with the most resources such as oil, natural gas, fertile soil, etc. will have an advantage over countries or businesses that don’t have as many resources.
- Technology: Countries with technologies will have more output than countries that don’t have as much technology. The time of production is reduced and the cost of production (such as paying wages or salaries to the workers) would be reduced.
- Knowledge: Countries or businesses with the best knowledge (e.g., in science, engineering, and business management) will have an advantage over countries or businesses that don’t have as much knowledge.
Importance
If a country or business has an absolute cost advantage over its competitors, it can charge more for its products and still make a profit. This allows companies to stay ahead of the competition and increase their market share.
An example of how absolute cost advantage can be used in marketing is in the production of cars. Suppose a company has a better car than any other company in the market. This gives the company an absolute edge over other companies in the market because it can charge more for its cars and still make a profit. This allows the company to stay ahead of the competition and increase its market share.
How can absolute cost advantage be achieved?
In order to achieve an advantage in any field, the following must be fulfilled:
- Cheaper source of resources or capital.
- Reduced production hours to the bearest.
- The cost of production is very low compared to others
- A small amount of input is used to achieve the same or better output than others
How businesses can measure their absolute cost advantage
- Benchmarking: Companies compare their performance against other similar companies in order to determine their advantage.
- Cost/benefit analysis: Countries or companies can evaluate their production cost compared to their competitors to determine if they have an advantage.
- Competitiveness index: Companies rank themselves according to factors such as innovation, quality, and customer service in order to determine their advantage.
- Productivity index: the number of outputs relative to the input can be used for comparison with competitors.
- Profitability: businesses can calculate how much profit they make relative to their expenses in order to determine their advantage.
- Leadership position: Companies measure how well they are positioned within their industry in terms of leadership and innovation in order to determine their advantage.
These are some common methods businesses use to measure their advantage over other businesses.
Examples of Absolute Advantage
Examples of absolute advantage can be explained using businesses or countries.
Absolute advantage examples in business
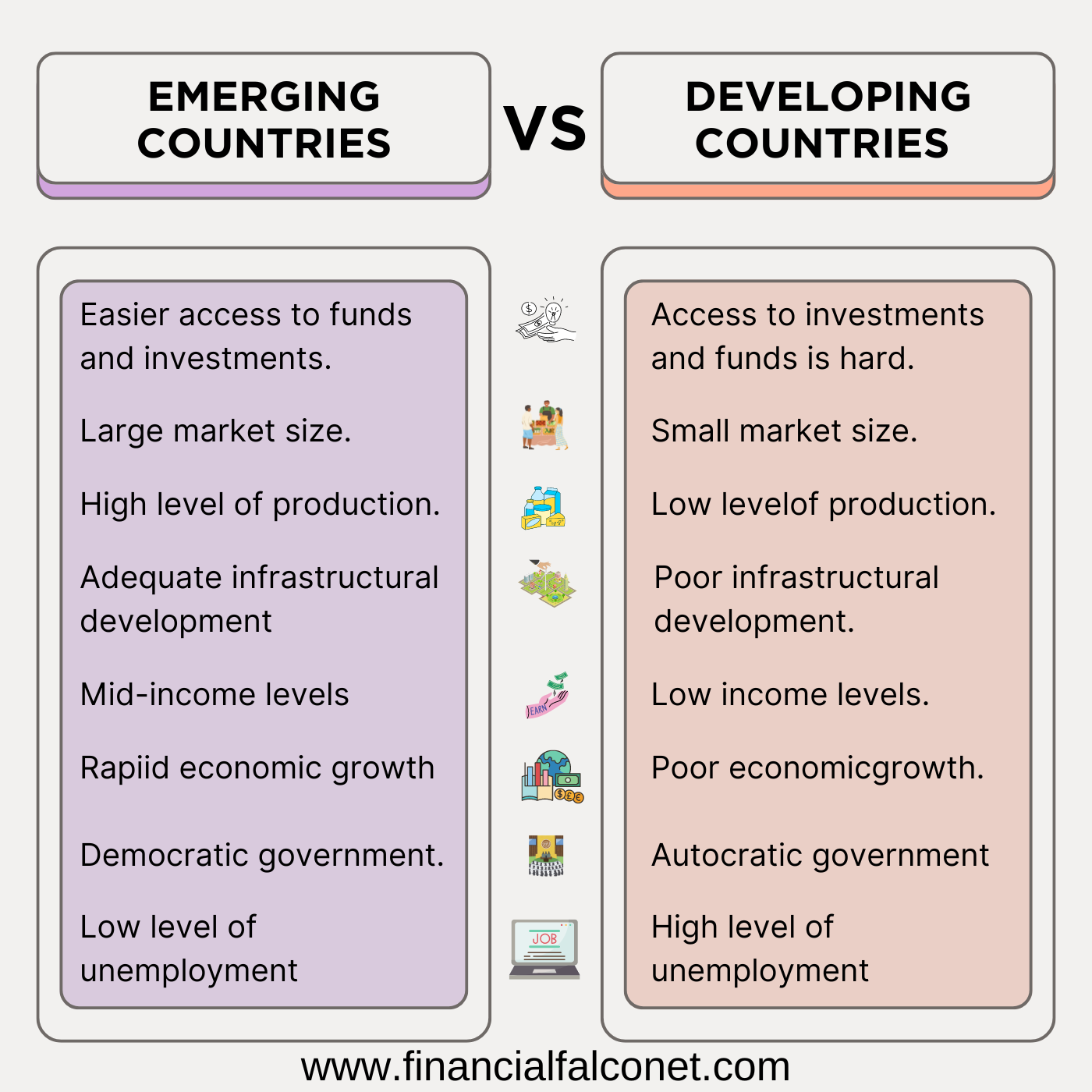
- Most businesses in developed nations have an absolute advantage over those in developing countries in terms of power supply. For example, Telecommunication networks in countries like Nigeria run generators 24 hours a day continuously; the cost of fuel and maintenance of these generators reduces the profit margin. Compare this to developed countries with regular power supply, this gives them an advantage over the developing nations.
- Google search engine has an absolute advantage over other search engines because it has most of the market share, is innovative, and has more skilled labor and resources compared to other search engines.
Absolute advantage examples for countries
- China has absolute cost advantage over most countries in terms of cheap labor; largely because of their population. Because of this, China can produce the same quality and more output of certain products such as clothing, footwear, toys, etc. at a lower cost than what is obtainable in other countries.
- Japan has an absolute advantage in the production of automobiles, electronics, computers, and most technological innovations. Japan’s absolute advantage in technology is mainly because of the number of robots used for production rather than humans. As of 2020, Japan has more than 300,000 robots that are used in its industries. This is the highest number of robots being used in industries compared to other countries of the world. This gives them an absolute cost advantage to produce more products at lower cost and in a shorter time.
- The United States’ absolute advantage is in technology and innovation. Most of the social media companies such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and other innovations in the internet sector such as google, bing, yahoo, etc. are all US companies. The US also enjoys another absolute cost advantage in the entertainment and media sector. This can be attributed to the highly skilled labor, presence of technology and innovation hubs such as Silicon Valley, abundant natural resources, effective and developed infrastructure, and high productivity.
- Switzerland has an absolute advantage over other countries in the banking and finance sector because of early internationalization, a high degree of competition, and flexible markets. It also has high wages and favorable tax rates. These factors all contributed to the development of the Swiss economy. The stability of the political system of Switzerland and government efficiency is very difficult for other countries to adopt.
- The absolute advantage of Russia is in the energy sector as it has the world’s largest natural gas reserves. In fact, it is the world’s leading natural gas supplier. Russia is regarded as an energy superpower because of the abundance of energy resources such as coal and crude oil.
There are many other countries that we may not give detailed information about as done above. But we will outline the names of the countries and their associated absolute cost advantage.
List of countries with absolute advantage
- Saudi Arabia has an absolute advantage in the production of crude oil
- Zambia has an absolute advantage in the mining of copper
- Colombia has an absolute cost advantage in growing coffee
- Germany’s absolute advantage is in engineering and technology.
- France’s absolute advantage is in nuclear energy. It is the world’s leading country in the production of nuclear energy. It has many nuclear energy companies such as Engie SA, Areva, and Électricité de France S.A. (EDF).
- South Africa has an absolute cost advantage in the mining of minerals such as platinum, chromium, and manganese.
How to calculate absolute advantage
There is no absolute advantage formula or equation. It is simply calculated by comparing the time it takes to produce a fixed amount of product. The country that uses the lowest time to produce the product has an advantage over the other. The same can be applied to the number of outputs using the same input; the country with more output from the same input has an advantage over the other.
Formula
We can give some examples using a table and then draw a simple absolute advantage graph to visualize how long it takes two countries to produce the same goods with the same input.
Consider the table below which records the number of hours it takes to refine 1 barrel of crude oil by the United Kingdom (UK) and Singapore.
| Input | The UK | Singapore |
|---|---|---|
| Production Hours | 5 | 2 |
| Barrel of crude oil | 1 | 1 |
From the table above, Singapore has an absolute cost advantage over the UK in refining crude oil because it takes it 2 hours to refine 1 barrel of crude oil while it took 5 hours for the UK to refine the same 1 barrel of crude oil.
Let us plot the graph as shown below.
Graph

Differences between absolute advantage vs comparative advantage
- The primary difference between absolute and comparative advantage is that comparative advantage takes into account the opportunity cost whereas absolute cost advantage does not.
- Comparative advantage looks at the mutual benefits between trading countries while absolute advantage favors only the country with the advantage.
- Comparative advantage looks at the profitability of activity as regards other opportunities that would be forfeited in order to achieve the current one; whereas absolute advantage does not take into account the profitability of the activity nor that of other opportunities forfeited. Absolute cost advantage only looks at the “who can do it better?“, that is, the capability between countries or businesses.